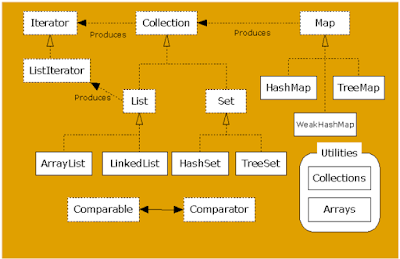
- A collection is a group of data manipulate as a single object.
- Collections are primarily defined through a set of interfaces.
- Interfaces are used of flexibility reasons
- Programs that uses an interface is not tightened to a specific implementation of a collection.
- It is easy to change or replace the underlying collection class with another (more efficient) class that implements the same interface.
- HashSet and TreeSet implement the interface Set.
- HashSet is much faster than TreeSet (constant-time versus log-time for most operations like add, remove and contains) but offers no ordering guarantees like TreeSet.
- HashSet
- Class offers constant time performance for the basic operations (add, remove, contains and size).
- It does not guarantee that the order of elements will remain constant over time.
- Iteration performance depends on the initial capacity and the load factor of the HashSet.
- It's quite safe to accept default load factor but you may want to specify an initial capacity that's about twice the size to which you expect the set to grow.
- TreeSet
- Guarantees log(n) time cost for the basic operations (add, remove and contains) .
- Guarantees that elements of set will be sorted (ascending, natural, or the one specified by you via its constructor) (implements SortedSet).
- Doesn't offer any tuning parameters for iteration performance
- Offers a few handy methods to deal with the ordered set like first(), last(), headSet(), and tailSet() etc.
- Important points:
- Both guarantee duplicate-free collection of elements.
- It is generally faster to add elements to the HashSet and then convert the collection to a TreeSet for a duplicate-free sorted traversal.
- None of these implementation are synchronized. That is if multiple threads access a set concurrently, and at least one of the threads modifies the set, it must be synchronized externally.
- LinkedHashSet is in some sense intermediate between HashSet and TreeSet. Implemented as a hash table with a linked list running through it, however it provides insertion-ordered iteration which is not same as sorted traversal guaranteed by TreeSet.
- So choice of usage depends entirely on your needs but I feel that even if you need an ordered collection then you should still prefer HashSet to create the Set and then convert it into TreeSet.
- e.g. SortedSet<String> s = new TreeSet<String>(hashSet);
Tuesday, 4 August 2015
Java Collection Set : Difference between Hashset and Treeset
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
No comments:
Post a Comment